CIS525 - Lecture#5 - September 20, 2000
CIS 525 LECTURE 5 9/20/00
"Introductory Articles" for a web site
1) executive overview
2) top-down
3) menu-like, (detailed table of contents)
4) search strategy
people tend to prefer short articles to long ones
Web site characterized by:
1) originator's identity, (individual, corporation, academic, non-profit)
2) originator's goals:
-sell products, (on-line, "e-tailer")
-advertise products
-inform/announce
-provide access
-offer services
-create discussion
-nurture community
Task support
-aggregate information and build knowledge support
1) short, unstructured list, (i.e. city guide)
2) linear structure, (i.e. calendar)
3) array or table
4) hierarchies/trees
5) multi-trees or faceted retrieval, (search within a search)
6) networks
Interface support:
metaphors to assist user
1) file cabinet w/folders and documents
2) books with chapters
3) encyclopedia with articles
4) television with channels
5) shopping mall with stores
6) museum with exhibits
'widgets' or 'handles' must be recognizable to the user to be effective
Design challenges:
website must be;
1) understandable
2) interesting and valuable
3) able to turn 'surfers' into 'users'
4) consistent and engaging
5) good integration of text, graphics, etc
6) easy to navigate
7) unified in its look and feel
Web presentations:
1st generation;
-content focused, (text based)
-content important, but it doesn't "sell" the web page
2nd generation;
-pages become flashy at expense of content
-LOTS of hyperlinks
3rd generation:
-attempt to balance;
=> effectiveness
=> Affectiveness, (to leave an impression on the user)
=> navigational ease
-requires deeper understanding of;
1) intended audience
2) purpose of web presentation
3) media qualities
4) hyperlinking information
4th generation:
-increased interactivity
-providing live access to content
-multi-media
-knowledge engineering, (data mining)
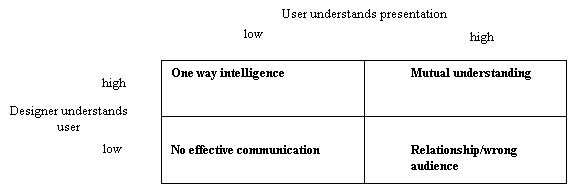 Purpose behind site:
1) entertainment
2) enable exchange, (buy, sell)
3) inform
Web creator's roles:
1) presenter, (client)
2) information steward, (maintains site)
3) designer
-understand information, (semantics)
-translate information into structure, (architectural design)
-translate structure into text and page
-artistic sense
-capacity for language selection, (vocabulary of text)
-familiar with multi-media technology
-some knowledge/familiarity with database, web access, security
Goal: determine user needs
-definition of expected information for each group of users
-statement of what web presentation will do
-list of information resources
Available techniques:
1) brainstorming
2) interviewing
3) virtual value chain analysis, (value added analysis)
4) web research
Defining information domain:
1) user centered approach
-determine groups and needs
2) information centered
-define and classify each piece of information
-information classified by potential user group
Information decomposition and structuring: (take ideas, make 'objects' or 'chunks')
after identifying 'chunks';
-> track them
a) list or outline
b) index cards
c) database
Information object relationships:
1) general to specific, ('is an example of...')
2) 'is-a' relationship, (super-sets)
3) associative relationship, ('peanut butter and jelly')
Web design process summary:
Purpose behind site:
1) entertainment
2) enable exchange, (buy, sell)
3) inform
Web creator's roles:
1) presenter, (client)
2) information steward, (maintains site)
3) designer
-understand information, (semantics)
-translate information into structure, (architectural design)
-translate structure into text and page
-artistic sense
-capacity for language selection, (vocabulary of text)
-familiar with multi-media technology
-some knowledge/familiarity with database, web access, security
Goal: determine user needs
-definition of expected information for each group of users
-statement of what web presentation will do
-list of information resources
Available techniques:
1) brainstorming
2) interviewing
3) virtual value chain analysis, (value added analysis)
4) web research
Defining information domain:
1) user centered approach
-determine groups and needs
2) information centered
-define and classify each piece of information
-information classified by potential user group
Information decomposition and structuring: (take ideas, make 'objects' or 'chunks')
after identifying 'chunks';
-> track them
a) list or outline
b) index cards
c) database
Information object relationships:
1) general to specific, ('is an example of...')
2) 'is-a' relationship, (super-sets)
3) associative relationship, ('peanut butter and jelly')
Web design process summary:
 Set up links to be:
-intrapage
-intranet
-intrasite
Set up links to be:
-intrapage
-intranet
-intrasite

