Now assuming that the algorithms have been implemented properly, the
computer can interpret visual image representations. One application of this
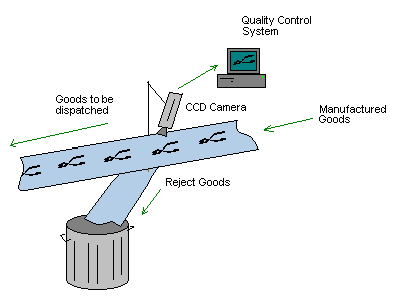
technology is quality control. Imagine an assembly line producing widgets.
Once the widgets are assembled, it passes on a conveyer belt with a digital
camera directly above it. As the widget passes by the camera on the conveyer
belt, the camera captures a picture of the widget. It now takes this image it
just received and compares it to the image of what a proper widget would look
like. If the computer sees any defects, bulges, dents, or irregularities in the
widget, it can immediately dismiss the widget as being defective. It could also
make sure that the widgets are all of a proper size, width, or height. The limits
are virtually non-ending. Another application for this technology could be a
self-guidance system. Imagine a camera attached to the front of a
self-operating cart. This camera could continuously take pictures to determine
itís current location, and the situation of objects around it. It could steer clear
of any obstacles in its way and guide itself through a building. Once finally
recognizing its final destination, the same way it recognized the proper
widgets, it could self dock itself and unload any cargo that may be in its
possession. 