CIS 4OO LECTURE 8
Declarations,
(continued):
·
Choice
representations
·
Storage
management
·
Generic
operators, (i.e. overloading operators)
·
Type
checking
Constants:
·
Literal
(i.e. "23")
·
Programmer
defined
v
Can
only simply defined variables be constants?
v
Can
expression assign values to constants?
v
When
is the value assigned?
v
Does
language specify pre-defined constants, (pi, e, 'maxint')?
Instances
of simple type:
·
Integer
·
Sub-range*,
(i.e. x := 0…100;)
·
Floating
point
·
Fixed
point*
·
Rational
numbers*
·
Complex
numbers*
·
Enumeration*
·
Boolean*
( * = not likely to have hardware support)
Issues:
·
Initialization
·
Conversion/
coercion, (compiler attempting to convert data type)
·
Static
and dynamic checking
®Structure type, (None of these are likely to have hardware support):
·
Vector
·
Multi-dimensional
arrays
·
Records,
('structs')
·
Strings
·
Files
·
Pointers
Issues
of structure type:
·
Specification
·
Operation
·
Implementation
v
Storage
representation, (sequential vs. linked)
v
Garbage/
dangling reference
v
Efficient
selection of components
·
Type
checking
v
Component
existence
v
Component
type
Data
control:
·
Language
features affecting…
v
Visibility,
(scope)
v
Accessibility,
(extent of variable º lifetime, i.e. from
allocation to deallocation)
v
Binding
between an identifier and data operator or sub-projects
Data
control concepts:
·
Reference
environments
v
Local
v
Non-local,
(i.e. 'friend', 'static', or header in C++. 'common block' in Fortran-SEE
BELOW)
v
Global
v
Pre-defined,
(pi, e, etc.)
·
Visibility
·
Dynamic
scope
·
Reference
operations-given an identifier and referencing environment, return associated
data object, (pointers, et al)
EXAMPLE OF NON-LOCAL REFERENCE ENVIRONMENT:
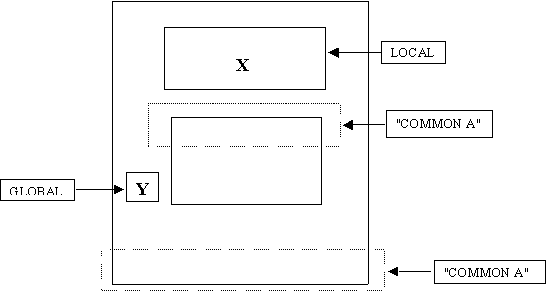
Data control issues:
·
Aliasing,
(more than one name or access path)
·
Dynamic
scope-most recent association rule, (run time)
·
Static
scope, (program text)

"Block structure" language scope rules,
(ALGOL):
·
Declarations
at the head of block define the local referencing environment for the block
·
References
outside block are assumed to be in next larger block
·
References
made to inner block identifiers are hidden from outer block
·
Block
may be named, reference becomes part of outer block referencing environment
2 choices upon block exit:
1)
Deletion
2)
Retention,
(history sensitivity)
Non-local referencing environments:
Explicit common:
·
Shared
block of data
·
Declarations
added to compiler table
Import/ export, (retention):
Procedure P(variables);
Define
x, y, z; // w, y, and z are made available for export
x, y, z
: real
u, v :
integer
begin
…
call Q
…
end
procedure Q(variables)
uses
P.x, P.z // looks at procedure P and imports x and z
y :
integer
begin
…
something happens
…
end