Lecture #1
CIS 400
9/8/99
(Sebasta Chapter 2)
IBM/
Backus (of
Backus-Naur form)
- Developed an algebraic translator
- Known as alligator clip programming
1° concern- Efficiency- object code
- Resources limited and hardware is
expensive
Fortran
0- designed 1954
Page 44 of text
http://www.engin.umd.umich.edu/CIS/course.des/cis400/fortran/fortran.html
- Compiler completed 1957
- Mostly using assembly languages
- Fortran 1 & 2 designed while the
Fortran 0 compiler was in development stage
1960
Fortran IV
page 47 of text
- Fixed fields in source code (columns 1-5
labels, 6 'continue', 7-72 source,
73-80 sequence fields)
|
Column # |
1–5 |
6 |
7 – 72 |
73 - 80 |
|
|
Labels |
Continue |
Source
code |
Sequence
fields |
- Implicit typing (I-N was integer variable types, all
else was floating point)
- Arithmetic 'if' Å, q , Æ
(>0, <0, =0)
- 'Do' iterator
- Formatted i/o
- Comments
1963 Naur developed Algol 60 ('root' for Pascal, PL/1, Ada)
page
55 of text
http://www.engin.umd.umich.edu/CIS/course.des/cis400/algol/algol.html
- 'Free' format (freedom of indentation,
spacing, etc)
- Reserved words (certain words could not
be variable names)
- Explicit typing (variable type had to be
explicitly defined)
- General iterator (similar to 'while')
- Block structure
- Recursive procedures
- Dynamic array bounds
- Value parameters
What is an "Algol-like"
language?
- Algorithmic language for describing
processes
- Imperative (most computation work done in assignment statements)
- Block & procedure
- Lexical scope
C Algol lexical scope
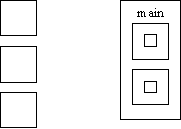
- Lexical scope is where the variable is
visible and allows nested subroutines
need
order
- Type checking
- Compilation used
also see
page 39 of text
Applicative language- functional
·
IBM in its
wisdom gave away FORTRAN with all its new computers creating wide spread
support for FORTRAN and undermining Algol support
·
Both
type-checking and scope was not so good in Algol, this resulted in reduced
reliability
·
Industry preferred
Fortran, academics preferred Algol
COBOL:
Page 61 of text
http://www.engin.umd.umich.edu/CIS/course.des/cis400/cobol/cobol.html
·
1959 Dept. of Defense
wanted a single language
·
1960 Remington
(Rand) developed the first compilers
·
Machine
independent
·
General if/then
else
·
'Noise' words
(almost English-like, so lowly accountants could follow programs i.e. they
didn’t have to know how to program to know what the code represented)
APL
Page 73 of text
IBM
1960 (Ken Iverson)
http://www.engin.umd.umich.edu/CIS/course.des/cis400/apl/apl.html
·
Very compact
notation for computation
·
Provided for
much matrix manipulation
·
NOT Algol-like
in nature
·
Originally
built to describe specifications of IBM360
LISP
Page 49 of text
http://www.engin.umd.umich.edu/CIS/course.des/cis400/lisp/lisp.html
Developed
at MIT, (and others) by John McCarthy, (graduate instructor of Dr. Modesitt!!)
AI is its application domain
·
Symbolic
expression, able to manipulate variable names like variable values (i.e.
pointer arithmetic)
·
Uniform
representation for expression (dataºcode) executable data structures.
·
New form of
conditional expression (similar to "switch" statements)
·
Pre-fix
expressions- operator followed by arguments
·
Recursion more
widely used
·
"Garbage
collection" used for data
management
·
A
"linked-list" type of structure is the basic structure in LISP