CIS 400 LECTURE 17:
Files
and I/O, (for ADT)
Sequence
·
Representation
on secondary storage device
·
Life
of data exceeds program
v
Sequential
access, ( i.e. #include <iostream.h>)
Vs.
v
Direct
access file, (file treated as an array), homogeneous data/base address offset
Components are called records
Sequential
files:
·
Some
linear sequence of components
·
Varying
length
·
Text
files organized by line, (at issue;what constitute end of line?)
·
File
position pointer, (from beginning of file)
Buffer-anticipates
next data need
Operations:
·
Open
·
Read
·
Write
·
End
of file, (eof)
·
Close
Sets,
(as a data structure):
·
Unordered
collection of distinct items
·
Operations
v
Membership
v
Insertion/deletion
of values
v
Union,
intersection, difference, complement, sub-set
Complexity
of searching any number of sets is big O(1)
Bit
string = 'd'
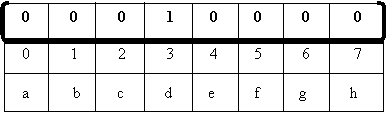
For
larger sets implementation:
® Hash table, (also big O(1))
® Linked lists
® Trees
Procedures:
Defined
by body
1)
Environment
2)
Code
BOTH
are "encapsulated", i.e. neither local data or statements in body are
separately accessible
Type
checking, (issues)
·
Arguments
and return values
·
Sometime
type checking is static, often it is not
·
Coercion
may or may not be provided
Two
varieties of procedures:
1)
Sub-routine:
changing parameter values is normal means of communication
2)
Function:
returns a single value
For
a given procedure there are 3 classes:
1)
Formal
parameters
2)
Local
variables
3)
Global
variables
3
key issues:
1)
Which
referencing environment is used to bind values?
2)
How
are actual parameters evaluated?
3)
How
are actual parameters bound to formal parameters?
Procedure
definition:
·
Written
by programmer at translation, (template for activation)
·
Procedure
activation-created during execution if procedure is invoked
·
Activation
life of procedure is from "call" to "return"
Implement
procedures and invocation:
·
Storage
for parameters
·
Storage
for function result
·
Storage
for local variables
·
Storage
for constants and literals
·
Storage
for executable
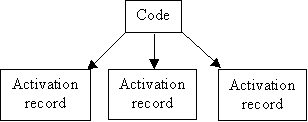
Static
part-doesn't change during execution, (code segment)
Dynamic
part-"activation record", (copies)
Code
segment:
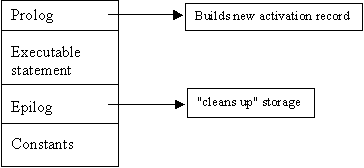
Activation
record:
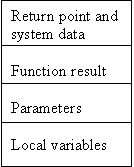
Stack
is the data structure for activation record
Simple
call and return
·
NO
recursive sub-programs
·
Requires
an explicit call statement
·
Procedures
execute completely with each call
·
Immediate
transfer of control at point, (copy rule)
·
Only
one module/procedure has control at a time, (execution is suspended)
CIP
º current instruction pointer
CEP
º current environment pointer
What
if you violate rule for no recursive procedures?
A ® B
// "A" cannot terminate before "B" returns
Co-routine
Procedures
that don't execute completely
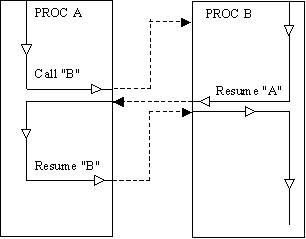
What
if you violate "immediate transfer of control" rule?
Schedule
procedure
·
"execute
at time__"
·
"execute
with priority 3"
uses
"clock" or "priority queue"
Tasks
More
than one thing runs at a time
Parameters
and parameter transmission
Argument
º actual parameter, (caller's name for
identifier)
Formal
parameter º procedure's name for
identifier
At
issue: are the above sharing values or addresses?
When
does the sharing take place?
1)
At
call
2)
At
first use
Correspondence
between formal and actual parameters?
·
Positional
correspondence, i.e. sort(10,a)
·
Correspondence
by explicit name, i.e. sort(N = 10, array = A)