CIS 400 LECTURE 15:
Pointers:
·
Address
of some kind
·
Operations:
creation, destruction, selection, equality testing
Types:
·
Refer
to data object of same type
·
Point
to any data type
Representation
of address:
·
"absolute"
address-actual location in memory
·
Alternatively,
it might be an offset from some base address
Design
issues:
·
Aliasing
problems, (several pointers to same object)
·
Garbage
collection
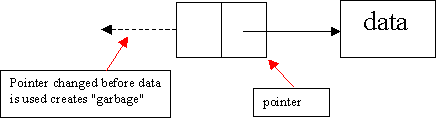
·
Dangling
references-retrieving storage without destroying access path, (MORE DANGEROUS
THAN GARBAGE CREATION)
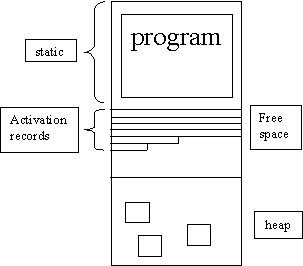
Storage
management:
Run-time
storage:
·
Code
segment-translated, user program
·
System
programs
·
User
defined data structures
·
Sub-program
return points
·
Referencing
environments
·
Temporaries
for expression evaluation
·
I/O
buffers
·
System
data
Operations:
·
Sub-program
call and return
·
Data
structures creation and destruction
·
Component
insert and delete
To
what extent should programmers be allowed to control storage allocation?
Problems:
·
Huge
burden on programmer to constantly implement delete functions
·
May
interfere with system storage maintenance
Storage
management phases:
·
Initial
allocation
·
Recovery
·
Compaction
and re-use
Storage
management techniques:
·
Static
storage management
v
Translation
time, (fixed at run-time), ALL STORAGE NEEDS MUST BE KNOW IN ADVANCE, no recursion is allowed, no dynamic memory
allocation
v
Very
efficient/not flexible
·
Stack
based run-time environment
v
Simplest
of all run-time techniques
·
Heap
based storage, (memory is allocated in pieces)
v
Fixed
size element techniques, every block the same size
v
Linked
list type stack:
Ø
Issues:
garbage collection and dangling references
Dangling
references:
·
"tombstone"-allocate
extra storage cell to point to block of storage
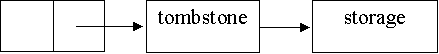
To
remove dangling reference, de-allocate storage and set "tombstone" to
nil
Advantages-prohibits
access to obsolete data
Disadvantages-time
costs
-space costs
·
"lock
and key"-2 passwords must match in order to access data
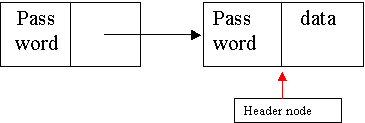
Advantages-prohibits
access to obsolete data
Disadvantages-storage
costs, (less than "tombstone")
Garbage:
·
Reference
count:
alloc
p //reference count increments by 1
pÙ = 3
alloc
q //reference count increments by 1
q =
p
dalloc
p //reference count decrements by 1
Program
waits until reference count is 0 before memory is returned to heap
Disadvantages:
costs associated with counter, (space, execution)
·
Garbage
collection, (NO dangling references)
Disadvantages:
drain on memory
When
free store becomes exhausted:
1.
Mark
active elements, (using check bit)
2.
Garbage
returned to free space
Marking
elements is difficult!!
Assumptions:
·
Active
elements must be reachable by chain of pointers beginning outside of heap
·
Must
be possible to identify every pointer outside heap that points to heap element
·
Must
be possible to identify any active heap element with fields pointing to other
heap elements