CIS 375 SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
University Of Michigan-Dearborn
Dr. Bruce Maxim, Instructor
Risks Analysis:
Kinds Of Risk:
Risk Projection
(or estimation):Risk Planner:
Date: 9/24/97
Week 3
Sample Impact Assessment Table:
|
CATEGORY \ COMPONENTS |
PERFORMANCE |
SUPPORT |
COST |
SCHEDULE |
|
|
|
1 |
Failure to meet would result in mission failure |
Failure results in increased costs and schedule delays with expected values in excess of $500K |
||
|
CATASTROPHIC |
2 |
Significant degradation to nonachievement of technical performance |
Nonresponsive or unsupportable software |
Significant, financial shortages, budget overrun likely |
Unachievable delivery date |
|
|
1 |
Failure to meet the requirement would degrade system performance to a point where mission success is questionable |
Failure results in operational delays and/or increased costs with expected value of $100K to $500k |
||
|
CRITICAL |
2 |
Some reduction in technical performance |
Minor delays in software modifications |
Some shortage of financial resources, possible overruns |
Possible slippage in delivery date |
|
|
1 |
Failure to meet the requirement would result in degradation of secondary mission |
Costs, impacts, and/or recoverable schedule slips with expected value of $1K to $100K |
||
|
MARGINAL |
2 |
Minimal to small reduction in technical performance |
Responsive software support |
Sufficient financial resources |
Realistic, achievable schedule |
|
1 |
Failure to meet the requirement would create inconvenience or nonoperational impact |
Error results in minor cost and/or schedule impact with expected value of less than $1K |
|||
|
NEGLIGIBLE |
2 |
No reduction in technical performance |
Easily supportable software |
Possible budget underrun |
Early achievable date |
Risk Projection:
{business, project, etc.}
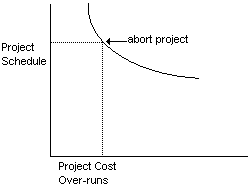
Risk Assessment:

{break even points - cost/schedule)
Risk Management (monitoring):
(No way to avoid risk)
Customer Questions