Programming Design
* Good programs
-= carries out task
-= correct
-= reliable
-= easily maintained
* Means to a good program
-= good structure
-= clear style
-= could be read top-down
-= clarity chosen over cleverness
* Top down design
-= develop plan in stages
-= delay data representation until
algorithm is complete
-= procedure interface defined first
-= no monolithic programming
-= program ideas written first in
pseudocode (blend of programming language and native tongue)
* Craps algorithm
(pseudocode)
-= call initialize (amount)
-= finish = "no"
-= while (finish != "no")
-= call accept bet (bet, amount)
-= call play
-= call update (bet, amount, won)
-= output "done"
-= input finish
-= end while
-= end craps
* Sub procedure (play)
-= output "how much will you bet?"
-= input bet
-= while (bet > amount)
-= output "can't bet that much,
broke guy, try another."
-= input bet
-= end while
-= call accept
-= (to test if accept bet is
working)
-= output "entering accept
bet"
-= output "amount = "
amount
Quality?
* Good solutions
-= clarity over cleverness
-= efficiency (execution time,
space, programming time)
-= reliability
- MTBF (mean time
between failures)
-= maintainability
- MTTR (mean time to
repairs)
-= system availability = MTBF
----------------
MTBF + MTTR
-= modifiability (future
growth)
-= flexibility (generality)
-= ease of use
* Black box (information
hiding)
-= implementation is unavailable to user
-= lends to development of
independent modules
Program Structure
* Implicit structure
* Referential structure
-= function calls
* Communication structure
-= data flow between statements
* Control structure
-= the way control changes between statements
* Lexical structure
-= actual layout
Design document
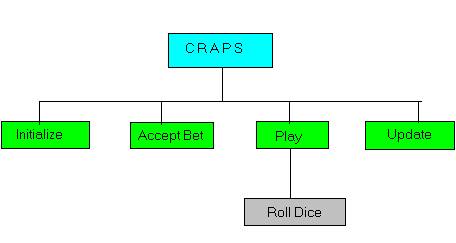
* Structure chart
* Module specifications
-= a single lower level box in the above diagram
* Data dictionary
Module
* Named entity
* Could be activated or used
by other modules
* When activated, it can
create data, objects, or perform work
* Can be compiled seperately
Module Specification
*module name
*module type
*functional description
*calling sequence
*preconditions/postconditions
*program state
*side effects
*errors and conditions
*pseudocode
Data Dictionary
* For each major data object
-= type name
-= attributes
-= information hiding
-= operations
-= module relationships
(interactions with other objects)
-= limitations/restrictions
Programming Teams
* egoless programming
(company owns rights)
* teams work faster
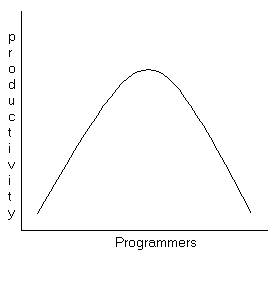
Productivity
curve
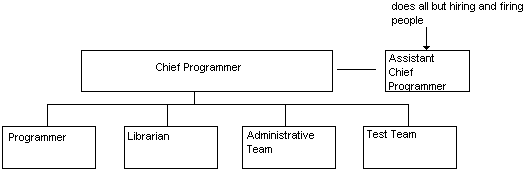
Hierarchy
of programming team
Structured Walkthroughs
* peer review of any product
-= code
-= diagrams
-= documents
* Why?
-= quality improves
-= catch design errors
early, not just coding errors ($)
-= enforce spirit of
standards
-= training/insurance
* Kinds of
walkthroughs
-= specification
-= design
-= code
-= test
Mechanics
* Presenter
* Coordinator
* Take notes (paper trail)
* Reviewers
-= quality
-= standards
-= interest of users
-= general review